3.1. Dr.Web for UNIX Internet gateways Components


|
3.1. Dr.Web for UNIX Internet gateways Components |



|
|
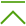
For UNIX Internet gateways protection, the following anti-virus components are provided: Dr.Web ICAPD Core component of Dr.Web for UNIX Internet gateways program complex. Allows to integrate it with HTTP/FTP-proxy server using ICAP protocol (usually this is server under protection that provides access to the Internet for LAN workstations). Console Dr.Web Scanner (can be managed on station only) Provides detection and neutralization of viruses on the local machine including shared directories. Dr.Web Daemon background monitor (can be managed on station only) Used by Dr.Web ICAPD component to check files and neutralizes threats, if possible. Quarantine Isolates malicious and suspicious objects in the special folder.
Dr.Web ICAPD module (drweb-icapd) allows integration of all Dr.Web for UNIX Internet gateways components with applications which use the ICAP protocol. This protocol is currently supported by Squid and SafeSquid proxy servers. Dr.Web ICAPD establishes connection between Dr.Web Daemon (drweb-daemon) and the corresponding proxy server to enable scanning of incoming FTP and HTTP traffic for viruses. It also allows filtering access to HTML resources by both the MIME type and size of downloaded files and the name of the host where these files reside. Moreover, it is possible to restrict access to webpages using regularly updated list of Internet resource categories, and white and black lists defined by the user (administrator of the suite). Interaction scheme: 1.Client requests an Internet resource (with a HTTP GET request). 2.Proxy server requests Dr.Web ICAPD a permission to access the required resource via the ICAP protocol. 3.If access to the requested resource is not forbidden (for example, if the user added the server to the white list, or this server is not included in the user-defined black list and in the list of Internet resource categories, or if the applied rules allow access to the resource), Dr.Web ICAPD allows the HTTP request for the proxy server. Otherwise, Dr.Web ICAPD instructs the proxy server to respond with an HTML page notifying that access to the requested resource is blocked. 4.If access to the remote server is allowed, the proxy server connects to it, receives response and then, via the ICAP protocol, transmits the received content to Dr.Web ICAPD for anti-virus scanning. 5.If the user added the remote server to the white list, the received content is not checked and Dr.Web ICAPD instructs the proxy server to transmit the content to the client. Otherwise, Dr.Web ICAPD checks the content with the use of content-filtering rules, and, if the rules instruct to apply a scan action, the content is transmitted to Dr.Web Daemon for anti-virus scanning. 6.According to the scan results, one of the following actions is applied to the requested content: a)pass—Dr.Web ICAPD allows the proxy server to return the requested content to the client. b)report—Dr.Web ICAPD instructs the proxy server to return generated HTML page notifying that the requested file is rejected. c)move—Dr.Web ICAPD moves the received file to Quarantine and instructs the proxy server to return generated HTML page notifying that the requested file is quarantined. d)truncate—an empty file is returned to the client. The same actions (except for moving to Quarantine) can be specified in content-filtering rules. Thus, you can instruct Dr.Web ICAPD to pass content of certain types (e.g. streaming video) without scanning, or, on the contrary, to reject it unconditionally. For that purpose, enable and configure the ICAP preview mode. For information on how to setup Squid and SafeSquid proxy servers for interaction with Dr.Web ICAPD, see the Dr.Web for UNIX Internet gateways Administrator Manual. |