Overview
Microsoft® Network Access Protection (NAP) is a policy enforcement platform built into Windows OS that allows you to better protect network assets by enforcing compliance with system health requirements.
With NAP, you can create customized health requirement policies to validate computer health in the following cases:
◆before allowing access or communication,
◆automatically update compliant computers to ensure ongoing compliance,
◆optionally confine noncompliant computers to a restricted network until they become compliant.
Detailed description of NAT technology specified at http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/us/nap-product-home.aspx.
NAP in Dr.Web Enterprise Security Suite
Dr.Web ESS allows you to use the NAP technology to check health of Dr.Web anti-virus software on protected workstations. This functionality is provided by use of Dr.Web NAP Validator.
Means of Health Validation
◆A NAP health policy server which is installed and configured in the network.
◆The Dr.Web NAP Validator which is an implementation of NAP System Help Validator (SHV) with use of Dr.Web custom policies plug-ins. This component is installed on the computer where the NAP server resides.
◆System Health Agents (SHAs) which are installed automatically on the workstations during installation of Enterprise Agents.
◆The Dr.Web Enterprise Server which serves as the NAP remediation server and ensures health of anti-virus software on workstations.
|
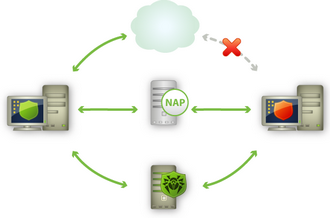
Diagram of the anti-virus network when NAP is used
Workstation Validation Procedure
1.Validation is activated when you configure the corresponding settings of the Agent. For more information, see Editing the Parameters of the Dr.Web Enterprise Agent.
2.The SHA connect to the Dr.Web NAP Validator installed on the NAP server.
3.The Dr.Web NAP Validator determines compliance of workstations against the health requirement policies as described below. To determine health compliance, NAP Validator checks workstation anti-virus state against the corresponding health requirement policies, and then classifies the workstation in one of the following ways:
◆Workstations which meet the health policy requirements are classified as compliant and allowed unlimited access and communication on the network.
◆Workstations which do not meet at least one requirement of the health policy are classified as noncompliant and have their access limited to Enterprise Server only. The Server allows noncompliant workstations to update the system with the necessary anti-virus settings. After update, the workstations are validated again.
1.Enterprise Agent must be started and running (Agent health).
2.Dr.Web virus databases must be up-to-date, i.e. databases on the workstation must be similar to those on the Server.
You need to configure Dr.Web NAP Validator after installing it on a computer where a NAP server resides. For more information on installation, see Installing NAP Validator.
To configure Dr.Web Nap Validator
1.To open NAP server configuration component, run the nps.msc command.
2.In the Policies section, select Health Policies.
3.Configure the NAP DHCP Compliant policy:
◆To enable the policy, select Dr.Web System Health Validator in the settings window.
◆To classify workstations as compliant only when all health policy requirements are met, select Client passed all SHV checks in the drop-down list.
4.Configure the NAP DHCP Noncompliant policy:
◆To enable the policy, select Dr.Web System Health Validator in the settings window.
◆To classify workstations as noncompliant if any of the health policy requirements are not met, select Client failed one or more SHV checks in the drop-down list.